Configuring S3 Service
3 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-12-12 11:00 -0500S3 allows you to connect to TrueNAS from a networked client system with the MinIO browser, s3cmd, or S3 browser.
Having large numbers of files (>100K for instance) in a single bucket with no sub-directories can harm performance and cause stability issues.
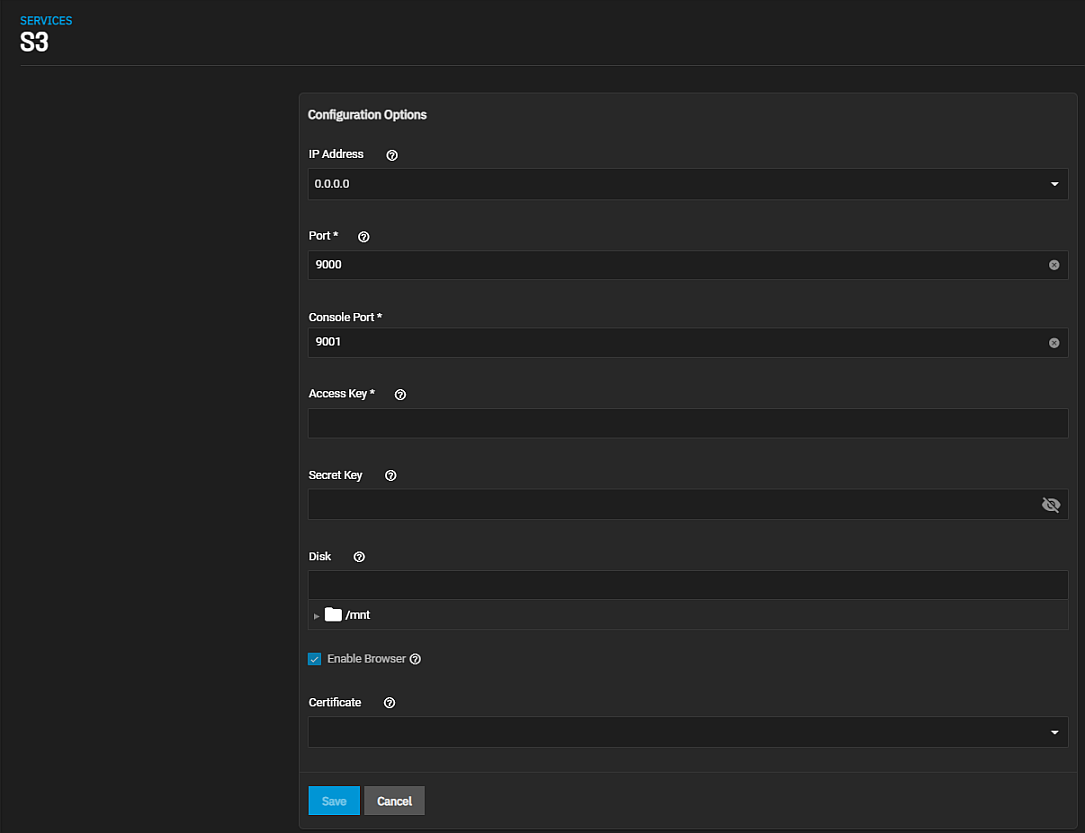
Go to the System Settings > Services and find S3, then click edit to open the Services > S3 screen to configure the service.
First, select a clean dataset, one that does not have existing data files. If you do not have a clean dataset, create a dataset. MinIO manages files as objects that you cannot mix with other dataset files.
Configure the remaining options as needed in your environment and start the service after saving any changes.
When Enable Browser is selected, test the MinIO browser access by opening a web browser and typing the TrueNAS IP address with the TCP port.
You must allow the port entered in the Services > S3 screen Port through the network firewall to permit creating buckets and uploading files.
Example: https://192.168.0.3:9000.
MinIO supports two different connection methods.
Linux or macOS users must have the s3cmd service installed before beginning this setup. On Windows, users can also refer to S3Express for a similar command-line experience.
Ubuntu or other Linux distributions can access the configuration by running s3cmd --configure to walk through critical settings.
Enter the specified access key and the secret key.
Enter the TrueNAS IP address followed by TCP port under S3 Endpoint, and reply N to the DNS-style bucket+hostname.
Save the file.
On Linux, the default is in the home directory
If the connection has issues, open nano .s3cfg or vi .s3cfg or gedit .s3cfg depending on the preferred text editor.
For other operating systems,
Scroll down to the host_bucket area and ensure the configuration removed the %(bucket)s. portion and the address points to the IP_address:TCP_port for the system.
Correct Example
host_base = `192.168.123.207:9000`
host_bucket = `192.168.123.207:9000`
Incorrect Example
host_base = `192.168.123.207`
host_bucket = `%(bucket)s.192.168.123.207`
Poll the buckets using s3cmd ls to see the buckets created with the MinIO browser.
For more information on using MinIO with s3cmd, see https://docs.minio.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio.html and https://s3tools.org/s3cmd.
The Windows PC S3 browser is another convenient way to connect to the MinIO S3 from TrueNAS.
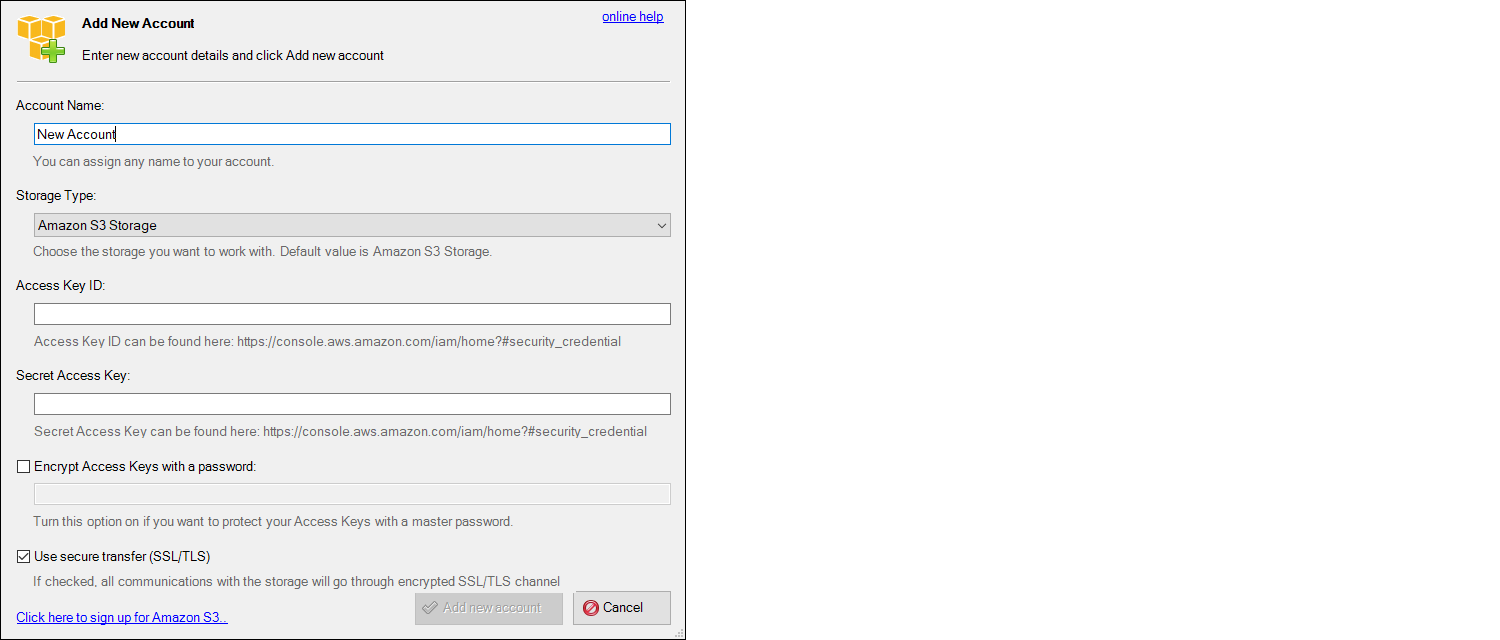
To set it up, first install the S3 browser.
After installation completes, add a new account.
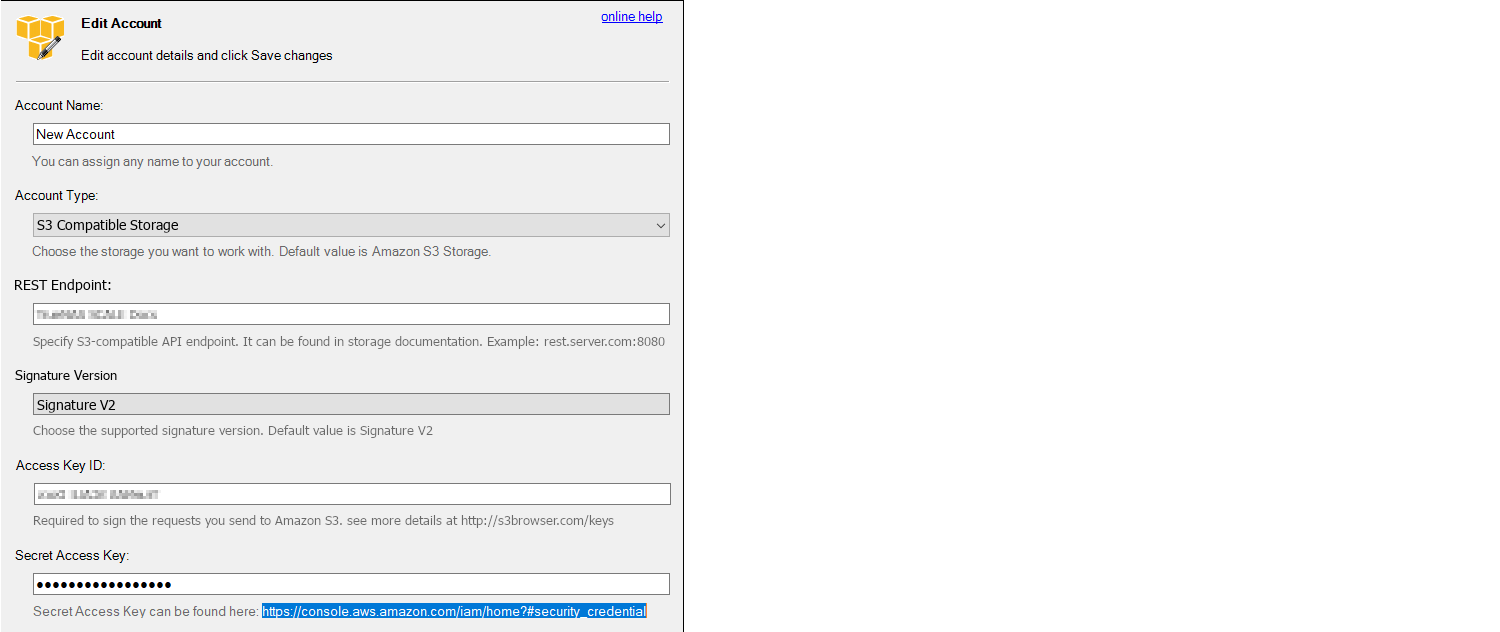
In the settings, select S3 Compatible Storage as the Account Type, then enter the MinIO access point similar to the s3cmd setup (TrueNAS_IP_address:9000 or other port if set differently).
Select the SSL settings appropriate for the particular setup.
The S3 browser assumes SSL by default, but it can be unset for a LAN attached session.
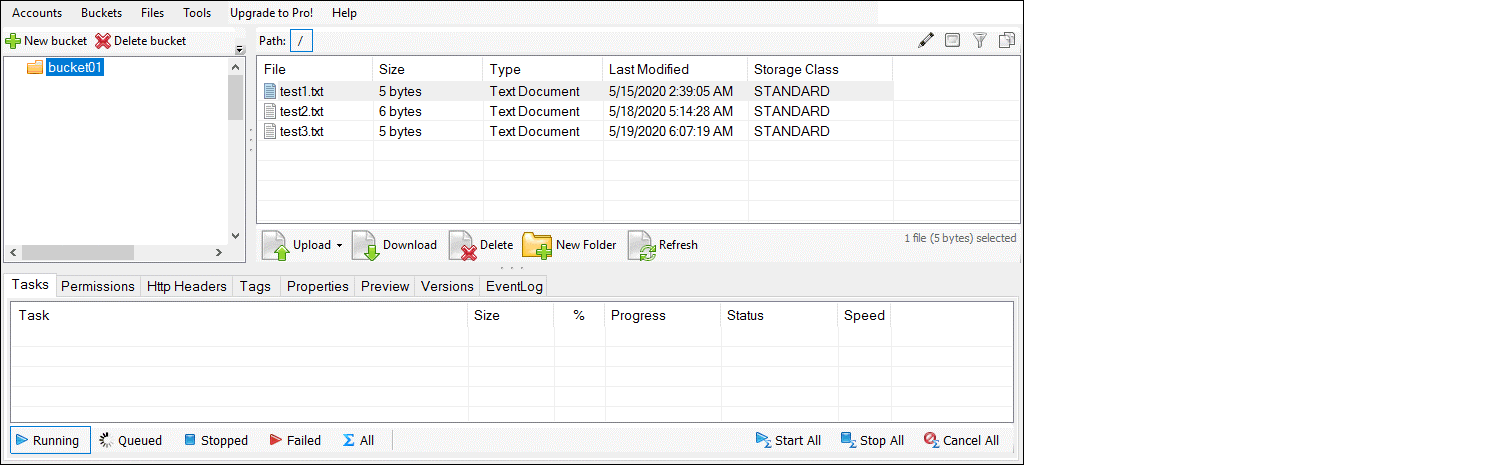
It is possible to access, create new buckets, or upload files to created buckets.