Adding NFS Shares
5 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-12-12 11:24 -0500Creating a Network File System (NFS) share on TrueNAS makes a lot of data available for anyone with share access. Depending on the share configuration, it can restrict users to read or write privileges.
Go to Shares > Unix (NFS) Shares and click Add to open the Add NFS configuration screen.
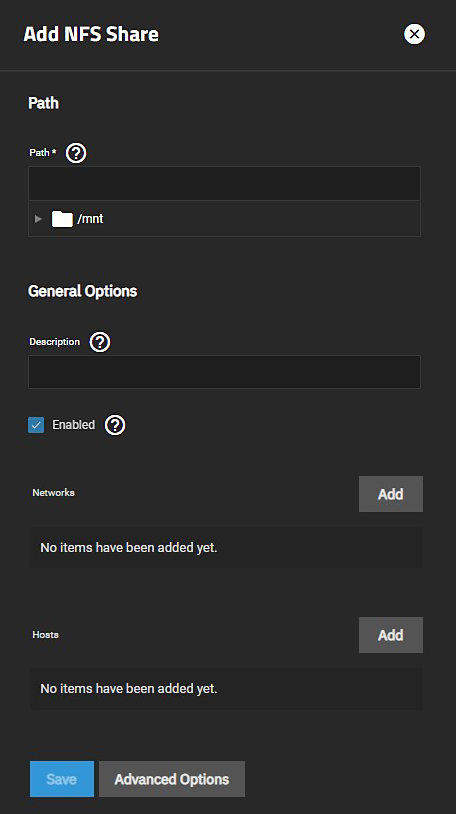
Click Add to display Add paths settings, and then enter the path or use the icon to the left of /mnt to locate the dataset and populate the path.
You can enter an optional text to help identify the share in Description. Click Save to create the share.
After adding the first NFS share, the system opens an enable service dialog.
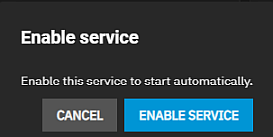
Enable Service turns the NFS service on and changes the toolbar status to Running. If you wish to create the share but not immediately enable it, select Cancel.
If you want to enter allowed networks, click Add to the right of Add Networks. Enter an IP address in the Authorized Networks field and select the mask CIDR notation. Click Add for each network address and CIDR you want to define as an authorized network. Defining an authorized network restricts access to all other networks. Leave empty to allow all networks.
If you want to enter allowed systems, click Add to the right of Add hosts. Enter a host name or IP address to allow that system access to the NFS share. Click Add for each allowed system you want to define. Defining authorized systems restricts access to all other systems. Leave the field empty to allow all systems access to the share.
If you want to tune the NFS share access permissions or define authorized networks, click Advanced Options.
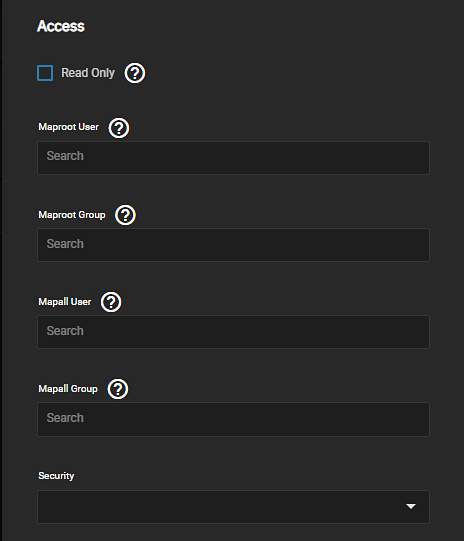
Select Read Only to prohibit writing to the share.
To map user permissions to the root user, enter a string or select the user from the Maproot User dropdown list. To map the user permissions to all clients, enter a string or select the user from the Mapall User dropdown list.
To map group permissions to the root user, enter a string or select the group from the Maproot Group dropdown list. To map the group permissions to all clients, enter a string or select the group from the Mapall Group dropdown list.
To edit an existing NFS share, go to Shares > Unix Shares (NFS) and click the share you want to edit. The Edit NFS screen settings are identical to the share creation options.
To begin sharing, click the on the toolbar displays options turn the NFS service on or off. Turn Off Service displays if the service is running or Turn On Service if the service is stopped.
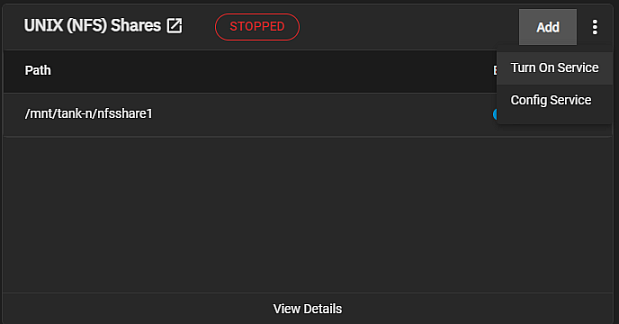
Or you can go to System Settings > Services, locate NFS and click the toggle to running. Select Start Automatically if you want NFS to activate when TrueNAS boots.
To configure NFS service settings click edit on the System Settings > Services screen.
Unless you need a specific setting, we recommend using the default NFS settings.
When TrueNAS is already connected to Active Directory, setting NFSv4 and Require Kerberos for NFSv4 also requires a Kerberos Keytab.
Although you can connect to an NFS share with various operating systems, it is recommended to use a Linux/Unix operating system.
First, download the nfs-common kernel module.
You can do this using the installed distribution package manager.
For example, on Ubuntu/Debian, enter command sudo apt-get install nfs-common in the terminal.
After installing the module, connect to an NFS share by entering command sudo mount -t nfs {IPaddressOfTrueNASsystem}:{path/to/nfsShare} {localMountPoint}.
Where {IPaddressOfTrueNASsystem} is the remote TrueNAS system IP address that contains the NFS share, {path/to/nfsShare} is the path to the NFS share on the TrueNAS system, and {localMountPoint} is a local directory on the host system configured for the mounted NFS share.
For example, sudo mount -t nfs 10.239.15.110:/mnt/Pool1/NFS_Share /mnt mounts the NFS share NFS_Share to the local directory /mnt.
You can also use the linux nconnect function to let your NFS mount to support multiple TCP connections.
To enable nconnect, enter command sudo mount -t nfs -o rw,nconnect=16 {IPaddressOfTrueNASsystem}:{path/to/nfsShare} {localMountPoint}.
Where {IPaddressOfTrueNASsystem}, {path/to/nfsShare}, and {localMountPoint} are the same you used when connecting to the share.
For example, sudo mount -t nfs -o rw,nconnect=16 10.239.15.110:/mnt/Pool1/NFS_Share /mnt.
By default, anyone that connects to the NFS share only has read permission. To change the default permissions, edit the share, open the Advanced Options, and change the Access settings.
ESXI 6.7 or later is required for read/write functionality with NFSv4 shares.

