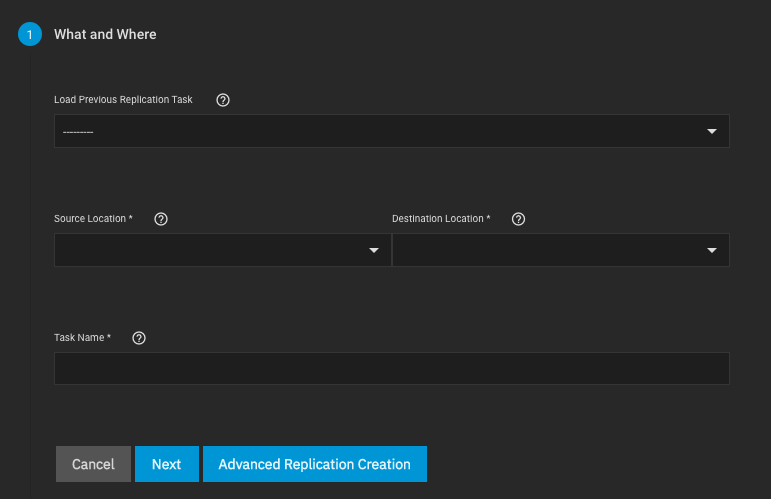
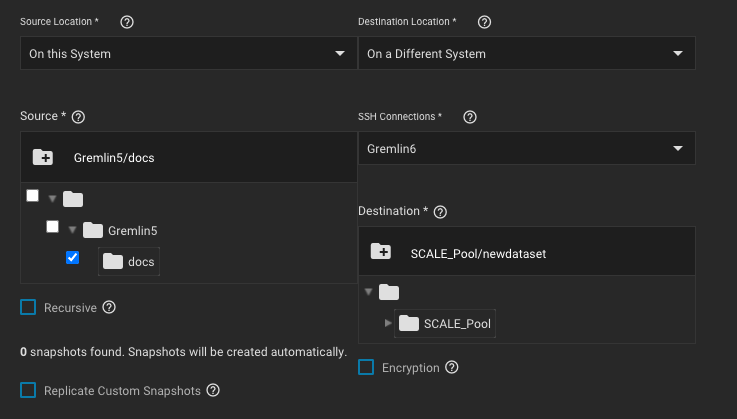
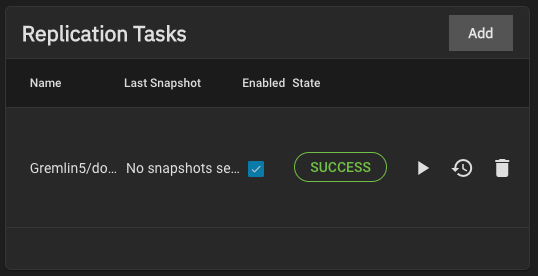
Start by configuring the replication sources.
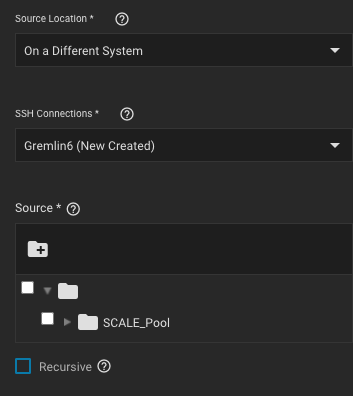
Sources are the datasets or zvols with snapshots to use for replication.
Choosing a remote source requires selecting an SSH connection to that system.
Expanding the directory browser shows the current datasets or zvols that are available for replication.
You can select multiple sources or manually type the names into the field.
TrueNAS shows how many snapshots are available for replication.
We recommend you manually snapshot the sources or create a periodic snapshot task before creating the replication task.
However, when the sources are on the local system and don’t have any existing snapshots, TrueNAS can create a basic periodic snapshot task and snapshot the sources immediately before starting the replication. Enabling Recursive replicates all snapshots contained within the selected source dataset snapshots.
Local sources can also use a naming schema to identify any custom snapshots to include in the replication.
Remote sources require entering a snapshot naming schema to identify the snapshots to replicate.
A naming schema is a collection of strftime time and date strings and any identifiers that a user might have added to the snapshot name.