MinIO Clusters
6 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-11-21 15:01 -0500On TrueNAS SCALE 20.12-ALPHA and later, users can create a MinIO S3 distributed instance to scale out and handle individual node failures. A node refers to a single TrueNAS storage system in a cluster.
In the images below, we used four TrueNAS systems to create a distributed cluster. For more information on MinIO distributed setups, refer to the MinIO documentation.
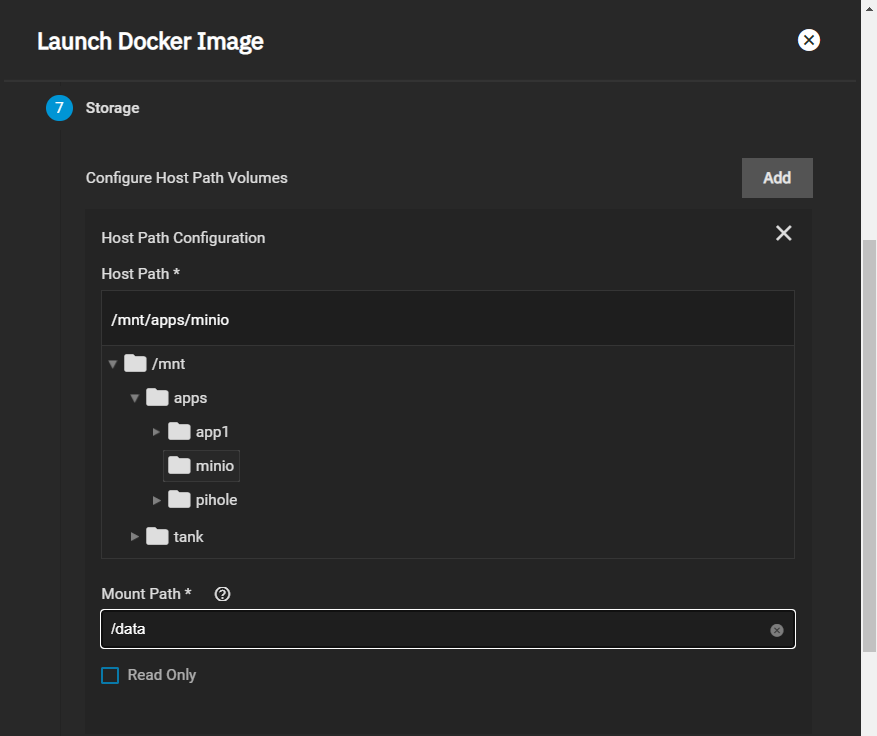
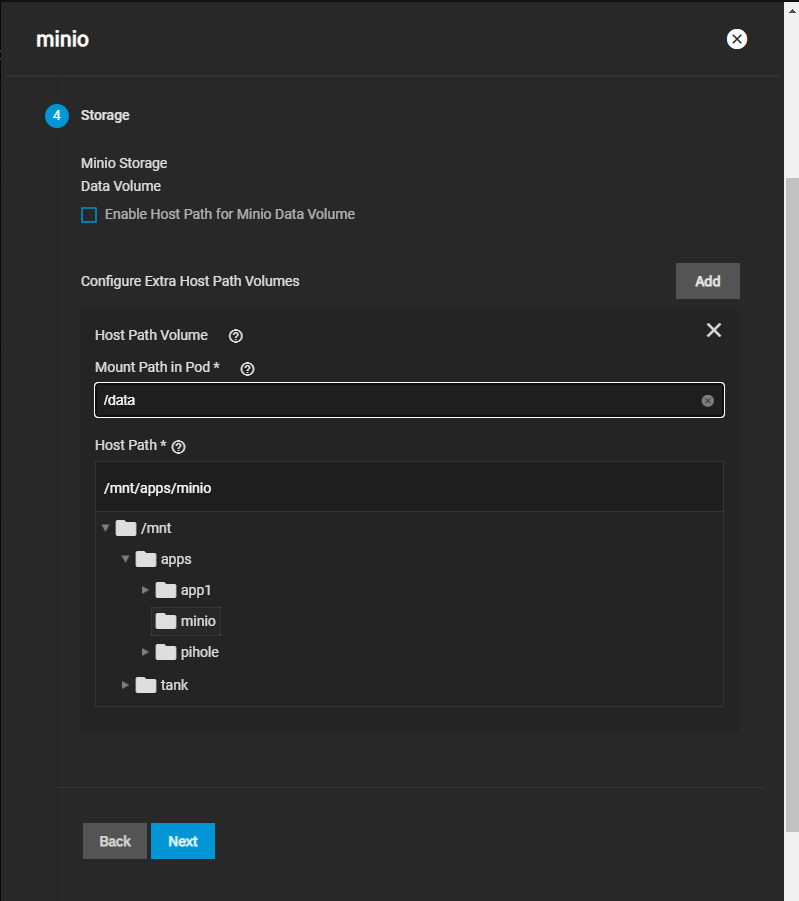
Before you configure MinIO, you must create a dataset and shared directory for the persistent MinIO data. Go to Storage > Pools and select the pool you want to place the dataset in. You can use an existing pool or create a new one.
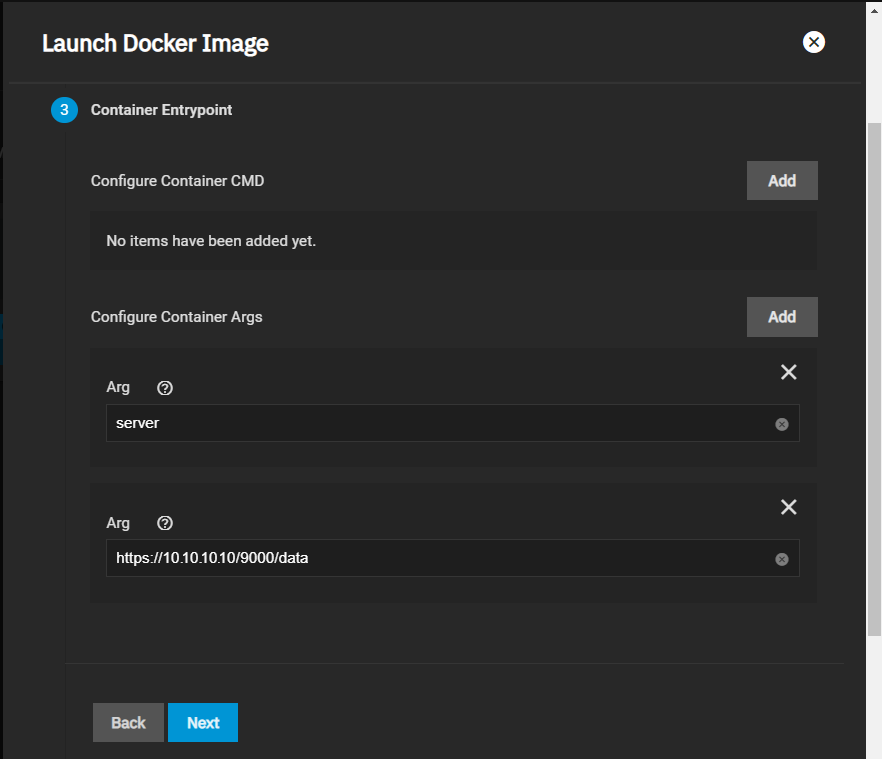
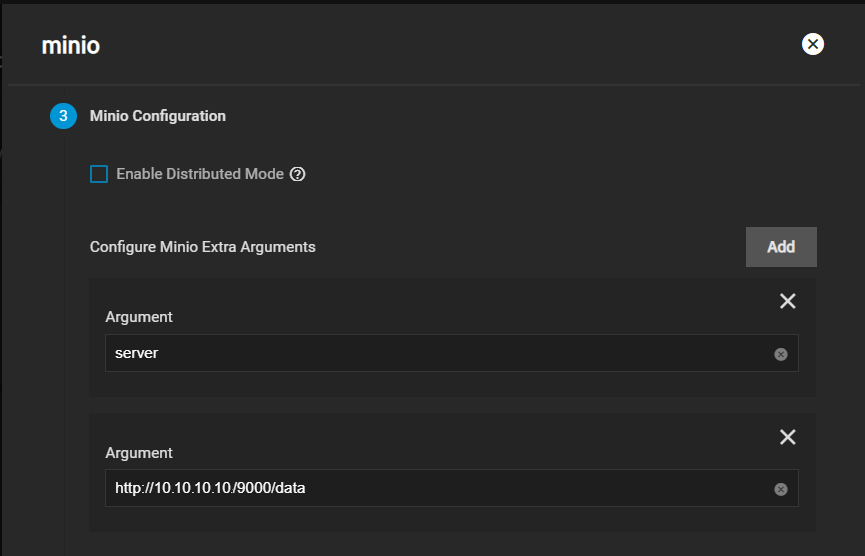
After creating the dataset, go to System > Shell and create the directory MinIO stores information the application uses. MinIO uses /data but allows users to replace this with the directory of their choice. Change to the /pool/dataset directory and then use the mkdir /mnt/data command to create the /data directory.
For a distributed configuration, repeat this on all system nodes in advance.
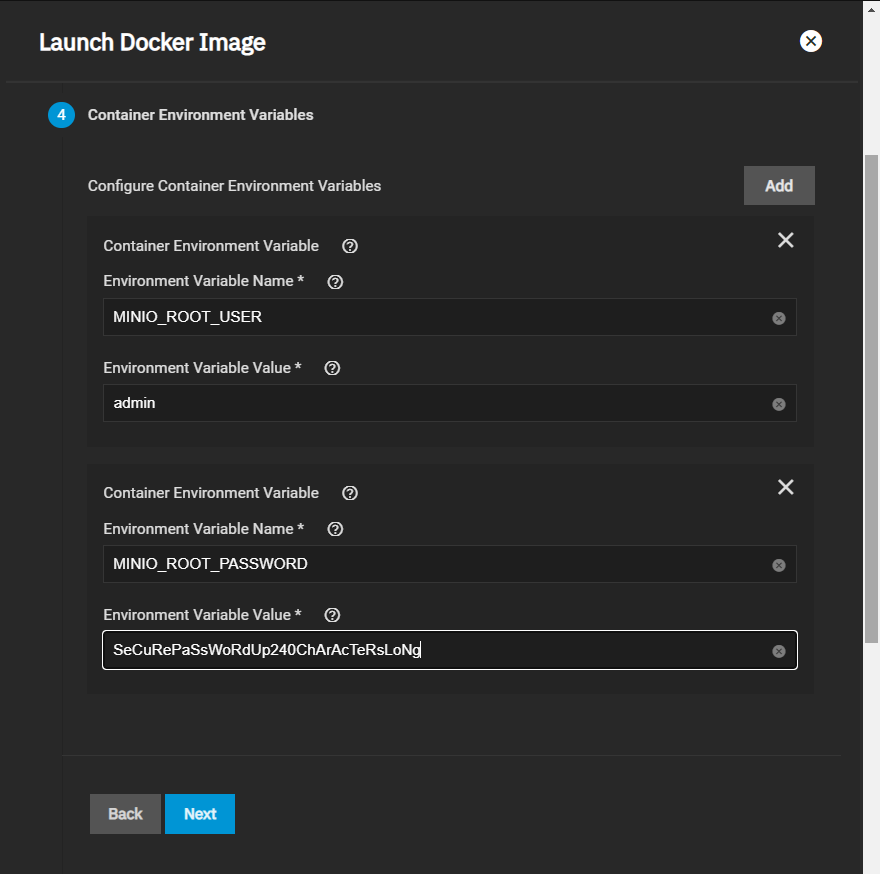
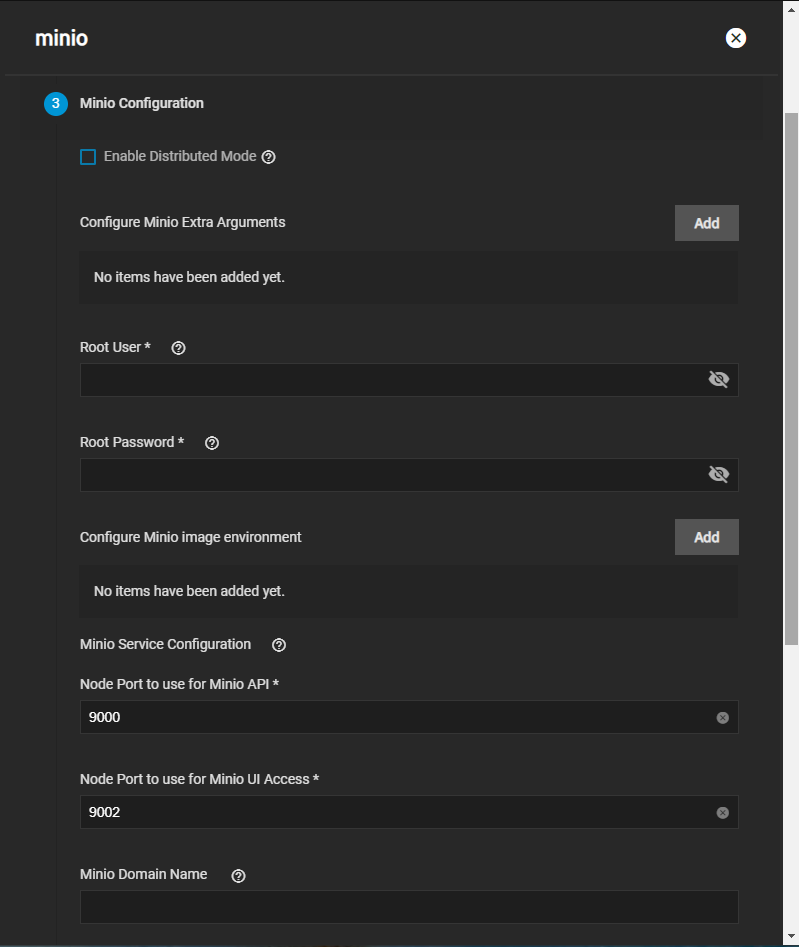
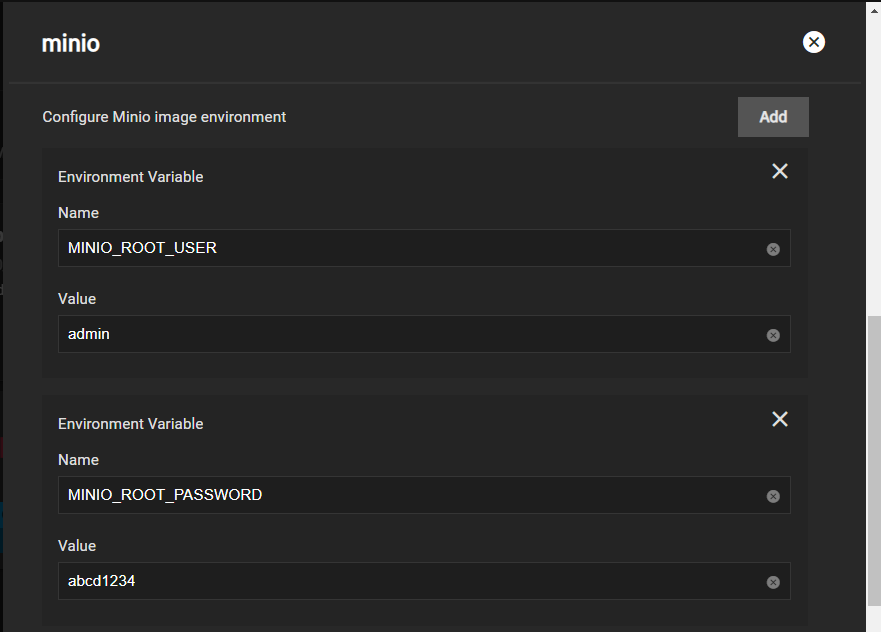
Note the system (node) IP addresses or hostnames and have them ready for configuration. Also, have your S3 username and password ready for later.
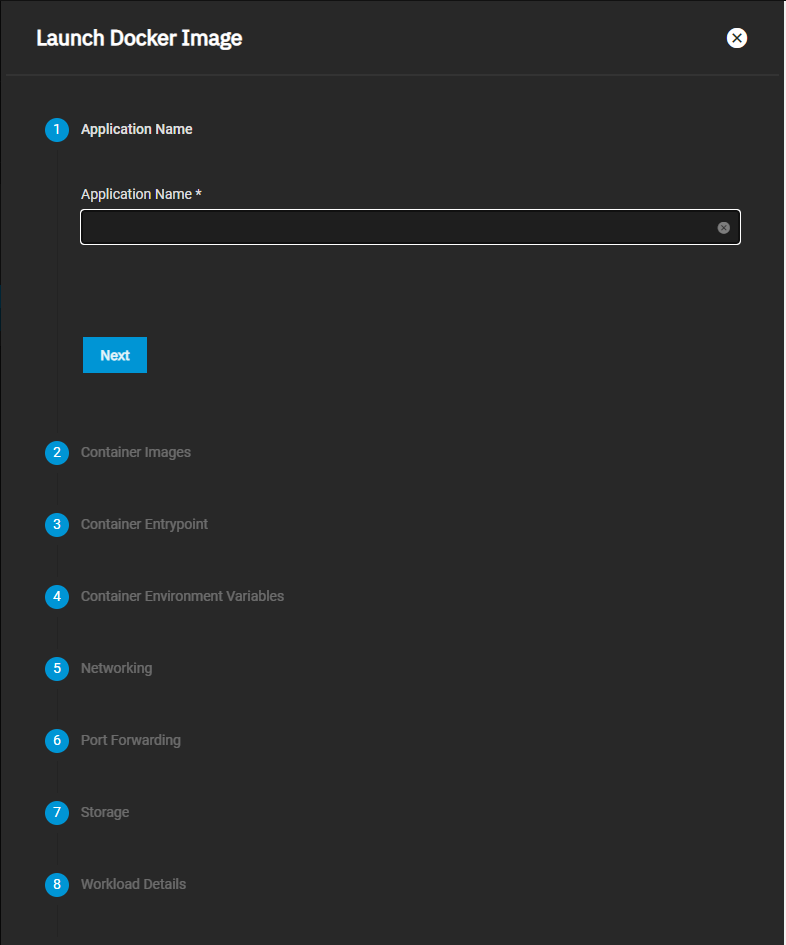
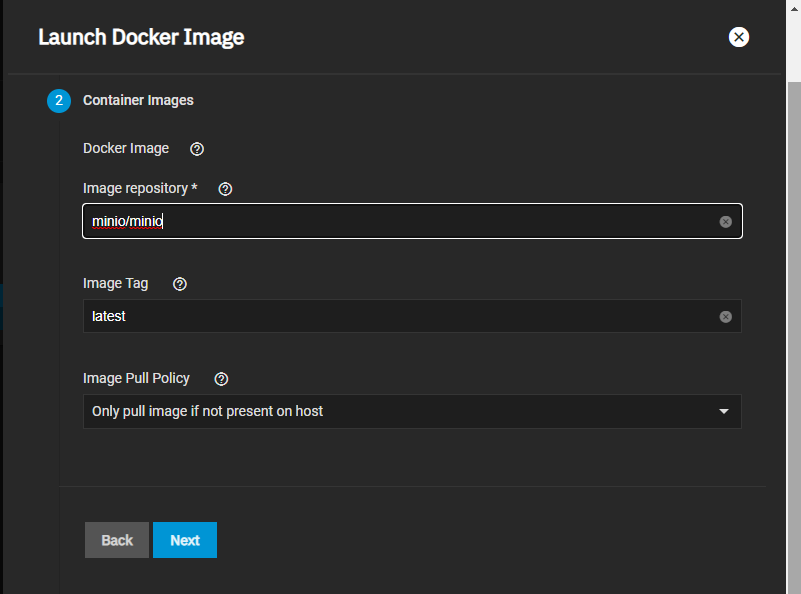
You can configure the MinIO application using either the Launch Docker Image button or the Install button on the MinIO application card on the Available Applications tab.
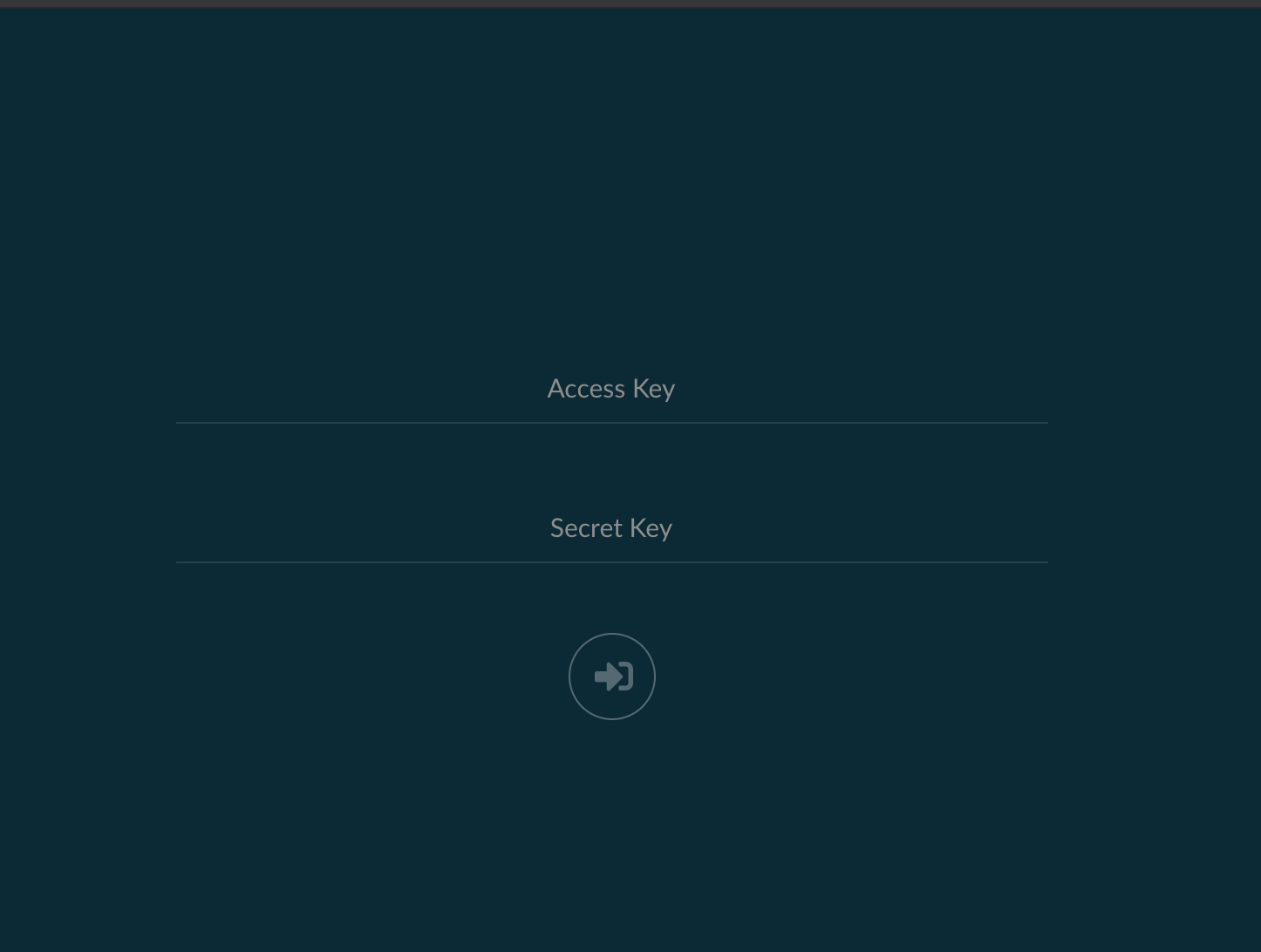
Once you’re done creating datasets, you can navigate to the TrueNAS address at port :9000 to see the MinIO UI. If you created a distributed setup, you can see all your TrueNAS addresses. Log in with the ROOT_USER and ROOT_PASSWORD keys you created as Container Environment Variables.