SMB Share Screen
9 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-08-11 09:23 -0400Server Message Block (SMB) is a file sharing protocol. Windows and other operating systems use SMB.
Go to Sharing > Windows Shares (SMB) to display the SMB screen and setup SMB shares on your TrueNAS.
Click Columns to change the information displayed in the table. Options are Unselect All, Path, Description, Enabled and Reset to Defaults.
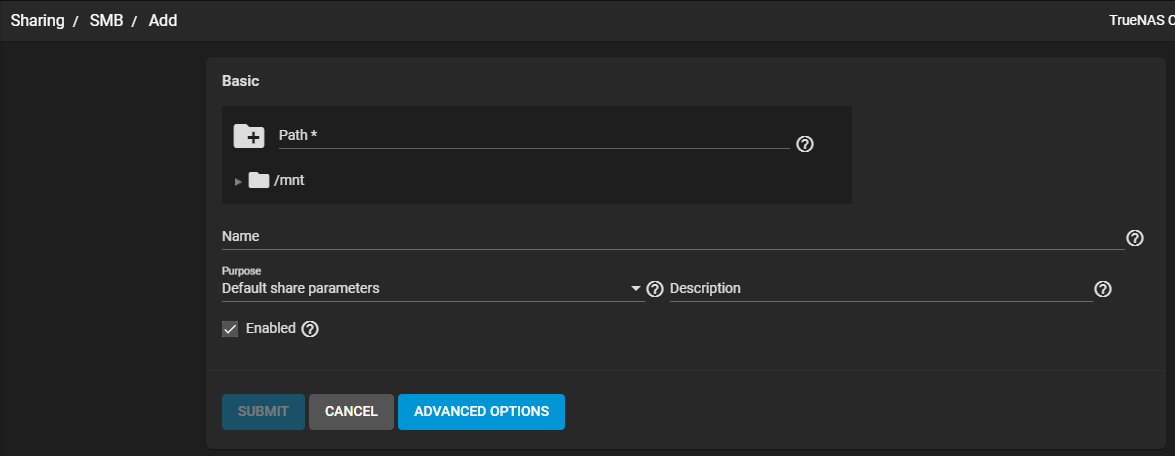
Click Add to display the BASIC Options settings screen.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Path | Use the file browser or click the /mnt to select the pool, dataset or directory to share. |
| Name | Enter a name for the SMB share. |
| Purpose | Select a preset purpose configuration. This locks in predetermined values for the share. This includes Advanced Options, as well as the Path Suffix. Select from the dropdown list. Options are: No presets Default share parameters Multi-user time machine Multi-protocol (AFP/SMB) shares Multi-protocol (NFSv3/SMB) shares Private SMB Datasets and Shares SMB WORM. Files become readonly via SMB after 5 minutes See “What do all the presets do?” for more information on presets. |
| Description | Optional. Explains the purpose of the share. |
| Enabled | Select to enable this SMB share. Clear checkbox to disable the share without deleting the configuration. |
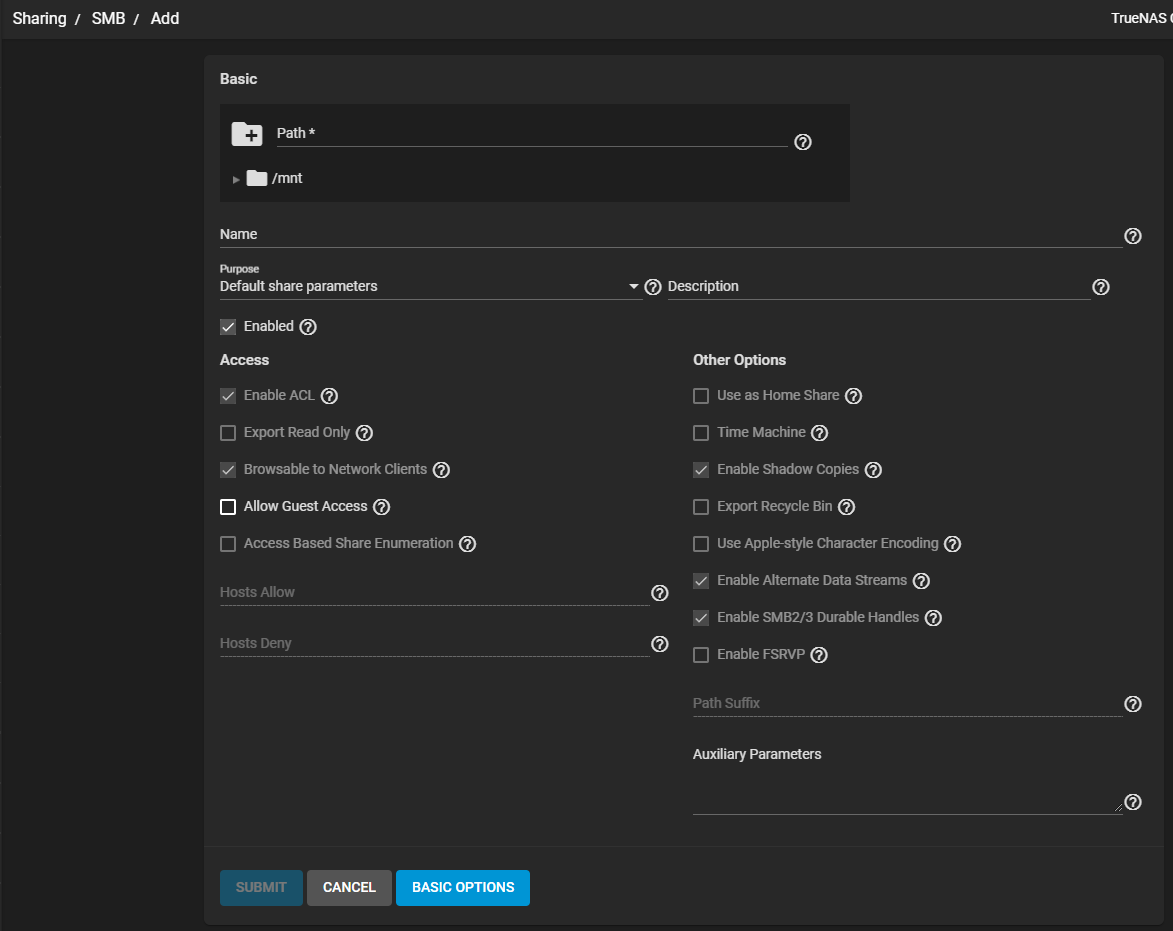
Access and Other Options are the two options groups. Access settings allow systems or users to access or change the shared data.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable ACL | Select to add Access Control List (ACL) support to the share. Leave checkbox clear to disable ACL support and delete any existing ACL for the share. |
| Export Read Only | Select to prohibit writes to the share. Leave checkbox clear to allow writes to the share. |
| Browsable to Network Clients | Select to include this share name when browsing shares. Home shares are only visible to the owner regardless of this setting. |
| Allow Guest Access | Select to make privileges the same as the guest account. Windows 10 version 1709 and Windows Server version 1903 have disabled guest access. Guest access for these clients requires extra client-side configuration. MacOS clients: Trying to connect as a user that does not exist in TrueNAS does not default to the guest account. The Connect As: Guest option must be specifically chosen in MacOS to log in as the guest account. See the Apple documentation for more details. |
| Access Based Share Enumeration | Select to restrict share visibility to users with read or write access to the share. See the smb.conf manual page. |
| Hosts Allow | Enter a list of allowed host names or IP addresses. Separate entries by pressing Enter. A more detailed description with examples see here. |
| Hosts Deny | Enter a list of denied host names or IP addresses. Separate entries by pressing Enter. |
The Other Options have settings for improving Apple software compatibility. There are also ZFS snapshot features, and other advanced features.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Use as Home Share | Select to allow the share to host user home directories. Gives each user a personal home directory when connecting to the share. This personal home directory is not accessible by other users. This allows for a personal, dynamic share. It is only possible to use one share as the home share. See the configuring Home Share article for detailed instructions. |
| Time Machine | Select to enable Apple Time Machine backups on this share. |
| Enable Shadow Copies | Select to allow export ZFS snapshots as Shadow Copies for Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) clients. |
| Export Recycle Bin | When selected, moves files deleted from the same dataset to the Recycle Bin. These files do not take any extra space. Deleting files over NFS is a permanent deletion! For files in a different dataset or a child dataset there is an extra step. These files are first copied to the dataset where the Recycle Bin is located. To prevent excessive space usage, deletes files larger than 20 MiB instead of moving them. Adjust the Auxiliary Parameter crossrename:sizelimit= setting to allow larger files. For example, crossrename:sizelimit=50 allows moves of files up to 50 MiB in size. This means files can be permanently deleted or moved from the recycle bin. This is not a replacement for ZFS snapshots! |
| Use Apple-style Character Encoding | Select to convert NTFS illegal characters in the same manner as MacOS SMB clients. By default, Samba uses a hashing algorithm for NTFS illegal characters. |
| Enable Alternate Data Streams | Select to allow multiple NTFS data streams. Disabling this option causes MacOS to write streams to files on the file system. |
| Enable SMB2/3 Durable Handles | Select to allow using open file handles that can withstand short disconnections. Support for POSIX byte-range locks in Samba is also disabled. This option is not recommended when configuring multi-protocol or local access to files. |
| Enable FSRVP | Select to enable support for the File Server Remote VSS Protocol (FSVRP). This protocol allows Remote Procedure Call (RPC) clients to manage snapshots for a specific SMB share. The share path must be a dataset mountpoint. Snapshots have the prefix fss- followed by a snapshot creation timestamp. A snapshot must have this prefix for an RPC user to delete it. |
| Path Suffix | Appends a suffix to the share connection path. This provides unique shares on a per-user, per-computer, or per-IP address basis. Suffixes can contain a macro. See the smb.conf manual page for a list of supported macros. The connectpath must be preset before a client connects. |
| Auxiliary Parameters | Additional smb.conf settings. |
Click Submit to save setings. This creates the share and adds it to the Sharing > Windows Shares (SMB) list.
Click CANCEL to exit without saving and return to the main SMB screen.

