Creating Rsync Tasks
5 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-09-23 10:02 -0400Rsync is a fast and secure way to copy data to another system, either for backup or data migration purposes. An rsync task requires configuration of both a Host and Remote system. These instructions assume a TrueNAS system for both the Host and Remote configurations.
Rysnc requires a dataset with the needed data on the Host or Remote system. Rsync provides the ability to either push or pull data. When using rsync to push, data copies from a Host system to a Remote system. When using rsync to pull, data pulls from a Remote system. It is then put on the Host system.
TrueNAS has extra requirements depending on if you choose the Module or SSH rsync mode.
Before you create an rsync task on the Host system, you must create a module on the Remote system. The Remote system must have rsync service activated. When TrueNAS is the Remote system, create a module by going to Services and clicking edit for the rsync service. Click the Rsync Module tab, then click ADD. See ConfiguringRsync for more information.
Log in to the Host system interface, go to Tasks > Rsync Tasks, and click ADD.
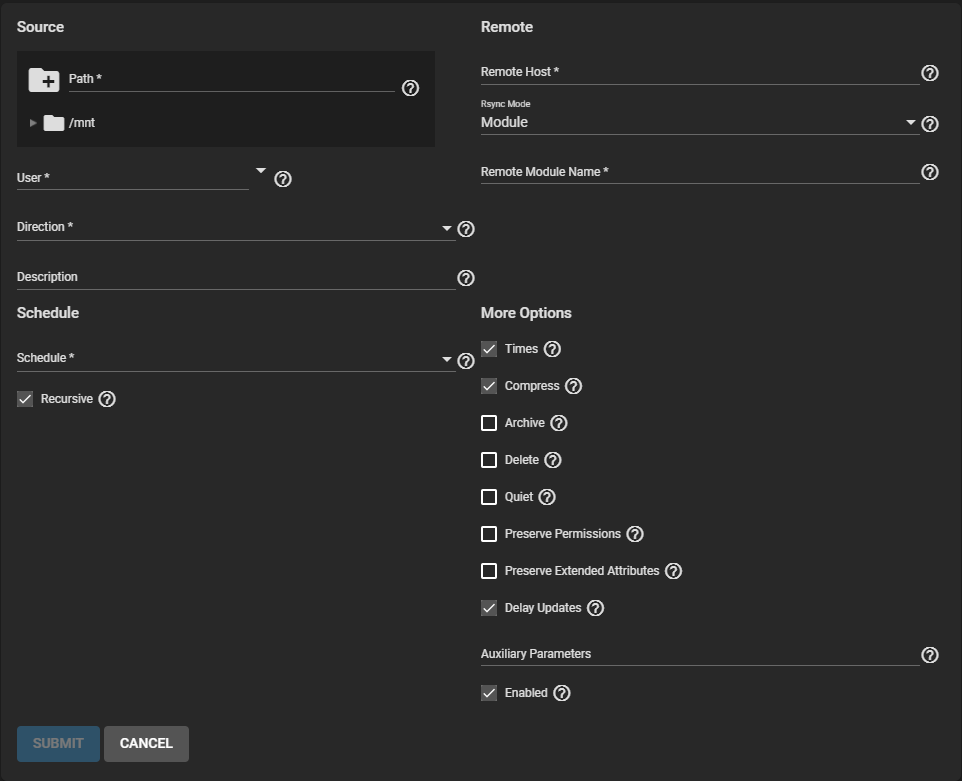
Select the Source dataset to use with the rsync task and a User account to run the rsync task. Select a Direction for the rsync task.
Select a Schedule for the rsync task.
Enter the Remote Host IP address or host name.
Use the format username@remote_host when the user name differs on the Remote host.
Select Module in the Rsync Mode dropdown list.
Enter the Remote Module Name as it appears on the Remote system.
Configure the remaining options according to your specific needs.
Clearing Enabled disables the task schedule. You can still save the rsync task and run it as a manual task.
The Remote system must have SSH enabled. To enable SSH in TrueNAS, go to Services and click the SSH toggle button. The toggle button turns blue when the service is on.
The Host system needs an established SSH connection to the Remote for the rsync task. To create the connection, go to System > SSH Connections and click ADD. Configure a Semi-automatic connection and from the Private Key dropdown list select Generate New.
Go to Tasks > Rsync Tasks and click ADD.
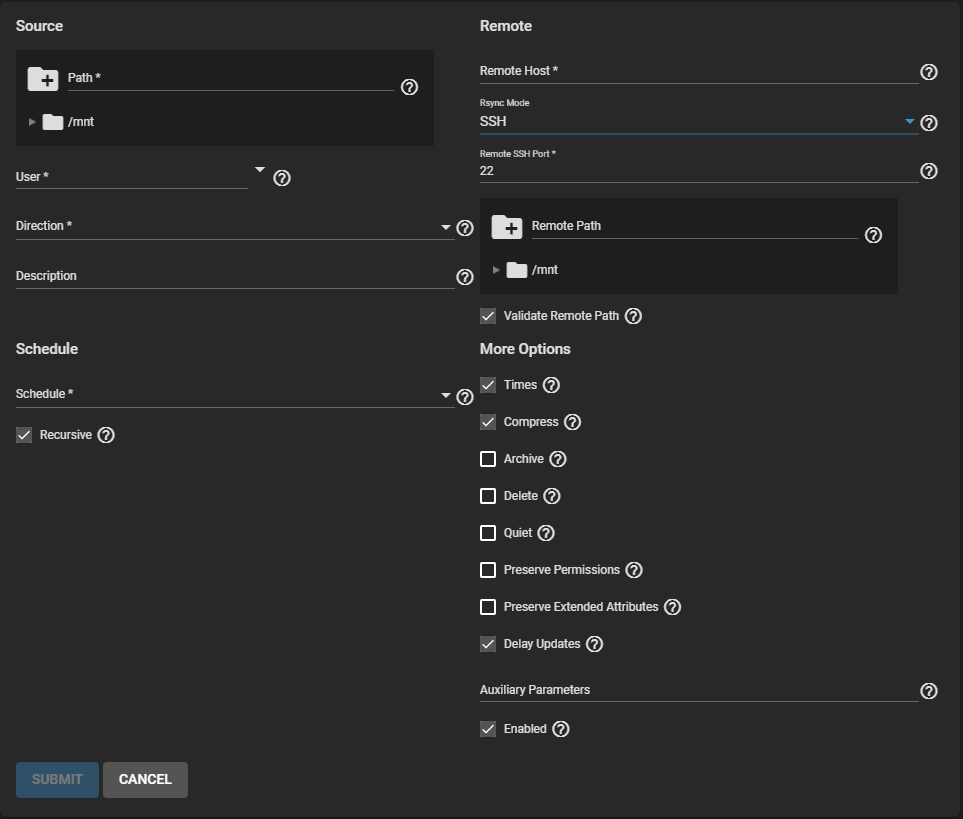
Configure the SSH settings first by selecting SSH in the Rsync Mode dropdown list. Enter the Port number and Remote Path.
Define the Source dataset for the rsync task and select an account in User. The name in User must be identical to the SSH Connection Username.
Select a direction for the rsync task, either Push or Pull, and define the task Schedule.
Enter the Remote host IP address or host name.
Use the format username@remote_host if the user name differs on the Remote host.
Configure the remaining options according to your specific needs.
Clearing the Enabled checkbox disables the task schedule without deleting the configuration. You can still run the rsync task by going to Tasks > Rsync Tasks and clicking , then RUN NOW.
The rsync task does not work when the related system service is off. To turn the rsync service on, go to Services and click the rsync toggle button. The toggle button turns blue when the service is on. See ConfiguringRsync for more information on rsync configuration and module creation.

