Advanced Replication
6 minute read.
Last Modified 2022-09-21 13:31 -0400Requirements:
- Storage pools with datasets and data to snapshot.
- SSH configured with a connection to the remote system saved in System > SSH Connections.
- Dataset snapshot task saved in Tasks > Periodic Snapshot Tasks.
To use the advanced editor to create a replication task, go to Tasks > Replication Tasks, click ADD to open the Wizard, then click ADVANCED REPLICATION CREATION.
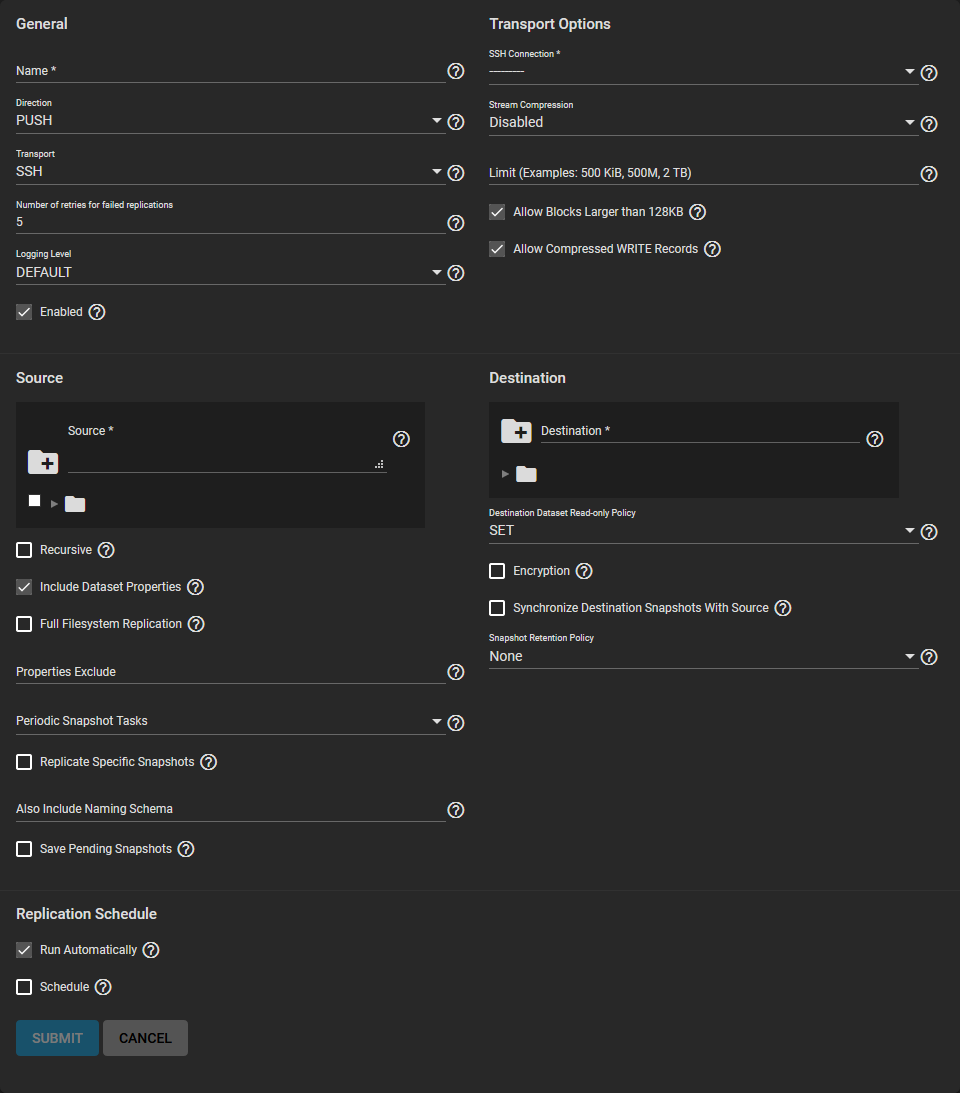
Options group by category. Options can appear, disappear, or be disabled depending on the configuration choices you make. Start by configuring the General options first, then the Transport options before configuring replication Sources and Destination.
Name the task. Each task name must be unique, and we recommend you name it in a way that makes it easy to remember what the task is doing.
Choose whether the local system is sending (Push) or receiving data (Pull) and decide what Transport method to use for the replication before configuring the other sections.
The Transport selector determines the method to use for the replication: SSH is the standard option for sending or receiving data from a remote system, but SSH+NETCAT is faster for replications within completely secure networks. Local is only used for replicating data to another location on the same system.
With SSH-based replications, configure the transport method by selecting the SSH Connection to the remote system that sends or receives snapshots. Options for compressing data, adding a bandwidth limit, or other data stream customizations are available. Stream Compression options are only available when using SSH. Before enabling Compressed WRITE Records, verify that the destination system supports compressed WRITE records.
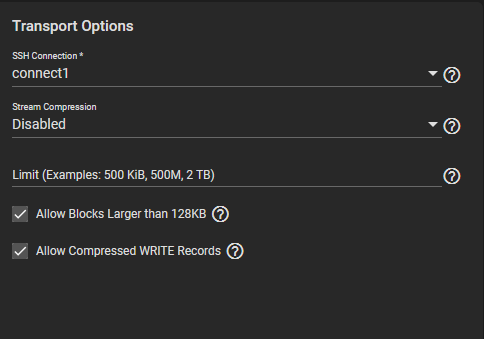
For SSH+NETCAT replications, you also need to define the addresses and ports to use for the Netcat connection.
Allow Blocks Larger than 128KB is a one-way toggle. Replication tasks using large block replication only continue to work as long as this option remains enabled.
The replication Source is the datasets or zvols to replicate. Select the sources for the replication task by opening the file browser or entering dataset names in the field. Pulling snapshots from a remote source requires a valid SSH Connection before the file browser can show any directories. If the file browser shows a connection error after selecting the correct SSH Connection, you might need to log in to the remote system and ensure it allows SSH connections. Go to the Services screen and check the SSH service configuration. Start the service.
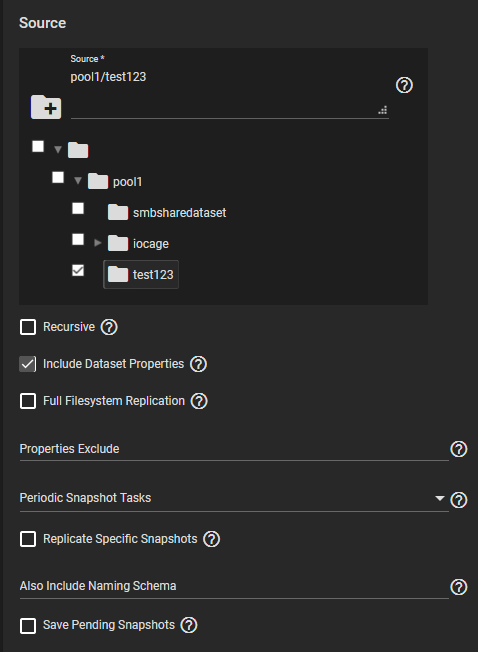
By default, replication tasks use snapshots to quickly transfer data to the receiving system. When Full Filesystem Replication is set, the chosen Source completely replicates, including all dataset properties, snapshots, child datasets, and clones. When choosing this option, we recommend allocating additional time for the replication task to run. Leaving Full Filesystem Replication unset but setting Include Dataset Properties includes just the dataset properties in the snapshots to be replicated. Additional options allow you to recursively replicate child dataset snapshots or exclude specific child datasets or properties from the replication.
Local sources replicate by snapshots you generated from a periodic snapshot task or from a defined naming schema that matches manually created snapshots.
Remote sources require entering a snapshot naming schema to identify the snapshots to replicate.
A naming schema is a collection of strftime time and date strings and any identifiers that a user might have added to the snapshot name.
For example, entering the naming schema custom-%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M finds and replicates snapshots like custom-2020-03-25_09-15.
Multiple schemas can be entered by pressing Enter to separate each schema.
To define specific snapshots from the periodic task to replicate, set Replicate Specific Snapshots and enter a schedule. The only periodically generated snapshots in the replication task are those that match your defined schedule. Alternately, you can use your Replication Schedule to determine which snapshots replicate by setting Run Automatically, Only Replicate Snapshots Matching Schedule, and defining when the replication task runs.
When a replication task has difficulty completing, set Save Pending Snapshots. Save Pending Snapshots prevents the source TrueNAS from automatically deleting any snapshots that fail to replicate to the destination system.
The destination is where replicated data is stored. Choosing a remote destination requires an SSH Connection to that system. Expanding the file browser shows the current available datasets on the destination system. You can click a destination or manually type a path in the field. Adding a name to the end of the path creates a new dataset in that location.
DO NOT use zvols for a remote destination
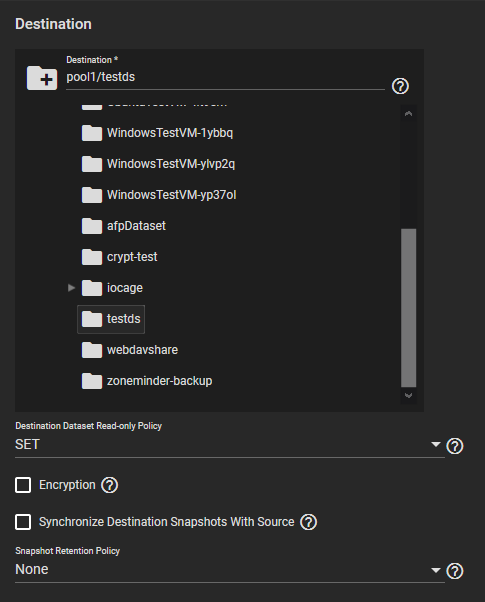
By default, the destination dataset is SET to be read-only after the replication is complete. You can change the Destination Dataset Read-only Policy to only start replication when the destination is read-only (REQUIRE) or to disable checking the dataset’s read-only state (IGNORE).
Encryption adds another layer of security to replicated data by encrypting the data before transfer and decrypting it on the destination system. Setting the checkbox allows using a HEX key or defining your own encryption PASSPHRASE. The encryption key can be stored in the TrueNAS system database or in a custom-defined location.
Synchronizing Destination Snapshots With Source destroys any snapshots in the destination that do not match the source snapshots. TrueNAS also fully replicates the source snapshots as if the replication task had never run before, which leads to excessive bandwidth consumption. This can be a destructive option, so be sure that any snapshots that the task deletes from the destination are obsolete or otherwise backed up in a different location.
Defining the Snapshot Retention Policy is generally recommended to prevent cluttering the system with obsolete snapshots. Choosing Same as Source keeps the snapshots on the destination system for the same duration as the defined snapshot lifetime from the source system periodic snapshot task. You can also define your own Custom lifetime for snapshots on the destination system.
By default, setting the task to Run Automatically starts the replication immediately after the related periodic snapshot task is complete.
Setting the Schedule checkbox allows scheduling the replication to run at a separate time.
Setting Only Replicate Snapshots Matching Schedule restricts the replication to only replicate those snapshots created at the same time as the replication schedule.


